Cloud Code Functions
For complex apps, sometimes you just need a bit of logic that isn’t running on a mobile device. Cloud Code makes this possible.
Cloud Code is easy to use because it’s built on the same Parse JavaScript SDK that powers thousands of apps. The only difference is that this code runs in your Parse Server rather than running on the user’s mobile device.
You can use Cloud Code to offload processing to the Parse servers thus increasing your app’s perceived performance. You can create hooks that run whenever an object is saved or deleted. This is useful if you want to validate or sanitize your data. You can also use Cloud Code to modify related objects or kick off other processes such as sending off a push notification.
When you update your Cloud Code, it becomes available to all mobile environments instantly. You don’t have to wait for a new release of your application. This lets you change app behavior on the fly and add new features faster.
This section explains how to create and deploy Cloud Code, followed by how to call a cloud function in Flutter projects through Back4App.
In this guide, the focus is to demonstrate the use of Cloud Function through Flutter. You can find more in-depth information in Parse Official Cloud Code Documentation.
To complete this tutorial, you will need:
- An Flutter app connected to Back4app.
- Note: Follow the Install Parse SDK on Flutter project to create an Flutter Project connected to Back4App.
- A device (or virtual device) running Android or iOS.
Run Parse Cloud Code on Back4App from a Flutter App.
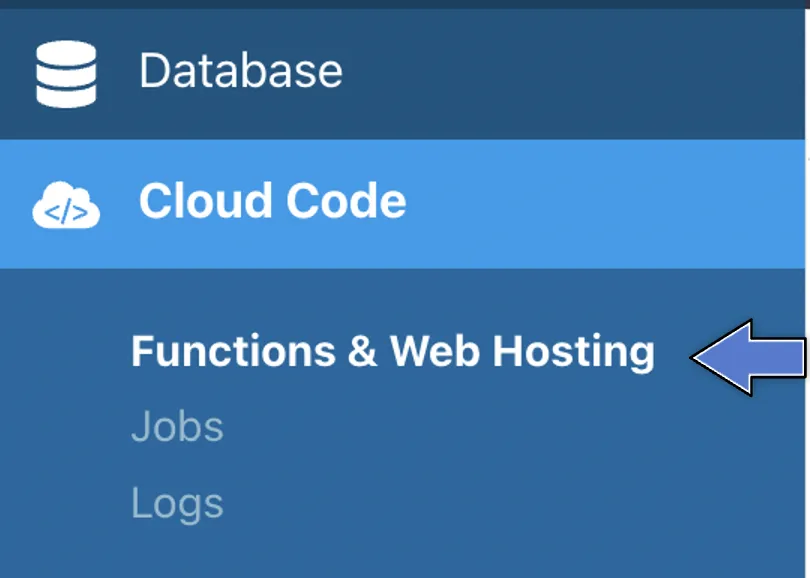
- Find the Cloud Code and click on Functions & Web Hosting. It looks like this:
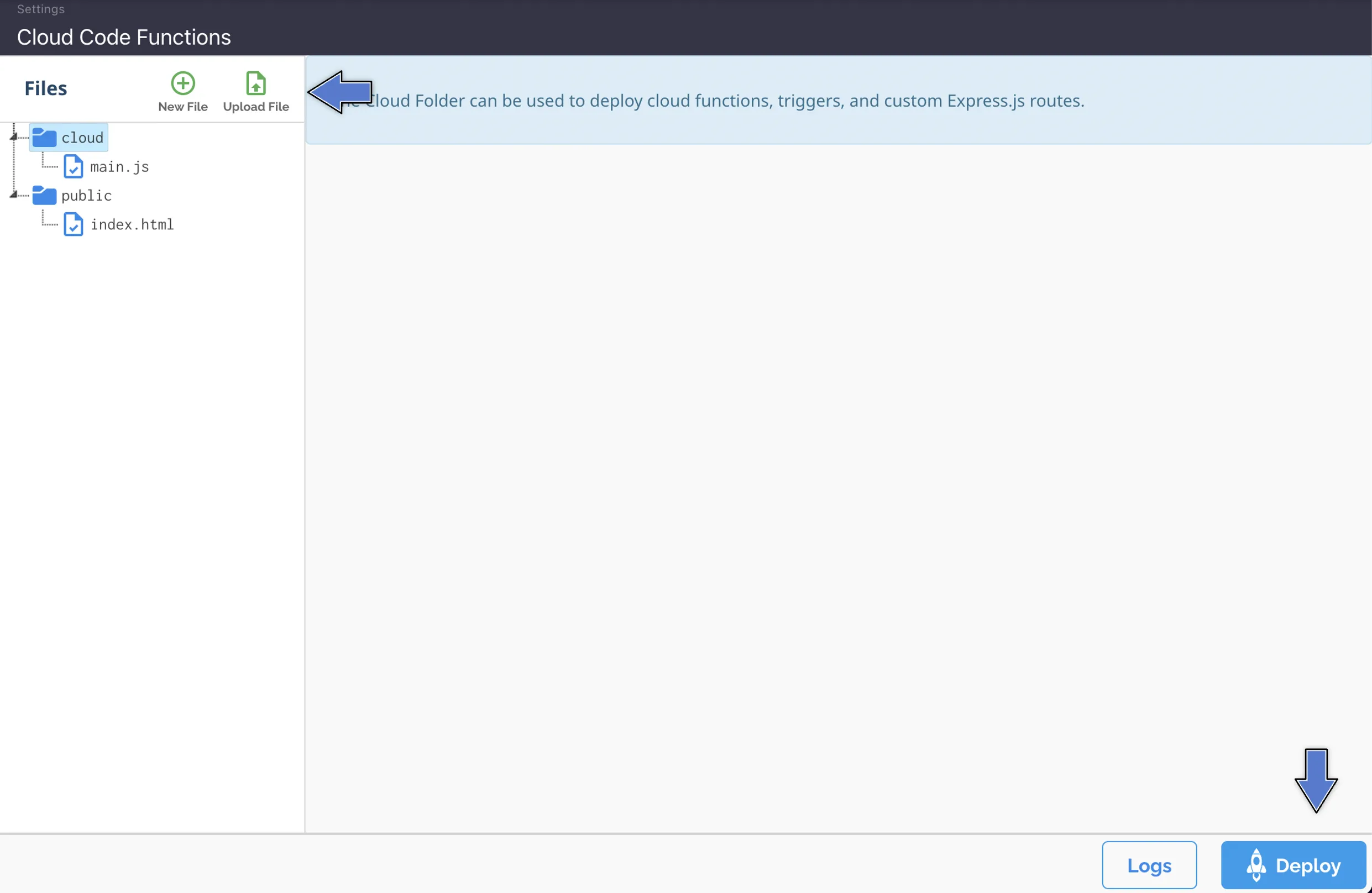
3. Upload or create a new file (you can also edit the currentmain.jsfile directly on the browser). Then, click at Deploy as shown here:
Yourmain.jsfile should look like this:
You pass parameters to your Cloud function from your Flutter App and access then within the request.params object.
The ParseCloudFunction class defines provides methods for interacting with Parse Cloud Functions.
A Cloud Function can be called with ParseCloudFunction.execute({parameters: params}) that returns a map object or ParseCloudFunction.executeObjectFunction<>({parameters: params}) that returns a ParseObject.
Parameters are optional and a map object is expected.
Now that you have deployed the Cloud Functions, we can call the functions using Flutter.
The result displayed in the console will be:
The result displayed in the console will be:
The result displayed in the console will be:
Example 4 - Call a Cloud Function that returns a list of maps that can be converted to a ParseObject
The result displayed in the console will be:
Let’s now use our example call cloud Function in Flutter App, with a simple interface.
Open your Flutter project, go to the main.dart file, clean up all the code, and replace it with:
Find your Application Id and Client Key credentials navigating to your app Dashboard at Back4App Website.
Update your code in main.dart with the values of your project’s ApplicationId and ClientKey in Back4app.
- keyApplicationId = App Id
- keyClientKey = Client Key
Run the project, and the app will load as shown in the image.
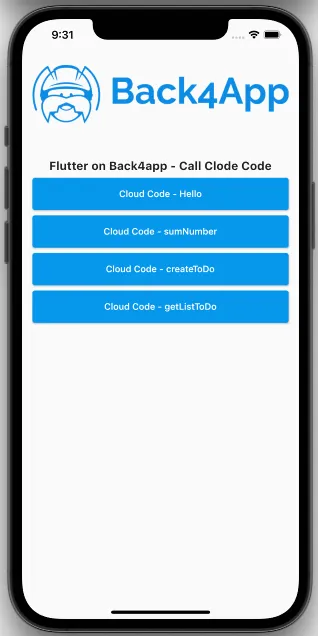
At this stage, you are able to code and call your own Cloud Code in your Flutter App using Parse Server Core features through Back4App!.