Relational Queries
In this guide, you will perform relational queries in Parse and implement a React Native component using these queries. You will learn how to set up and query realistic data using Back4App and React Native.
Query relational data stored on Back4App from a React Native App.
Any Parse query operation uses the Parse.Query object type, which will help you retrieve specific data from your database throughout your app. It is crucial to know that a Parse.Query will only resolve after calling a retrieve method (like Parse.Query.find or Parse.Query.first), so a query can be set up and several modifiers can be chained before actually being called.
To create a new Parse.Query, you need to pass as a parameter the desired Parse.Object subclass, which is the one that will contain your query results. An example query can be seen below, in which a fictional Book subclass is being queried.
You can read more about the Parse.Query class here at the official documentation.
Let’s create an assortment of classes, which will be the target of our queries in this guide. The classes are: Author, Book, Publisher and BookStore, in which Book has a 1:N relation with Publisher and N:N with Author, and BookStore has an N:N relation with Book.
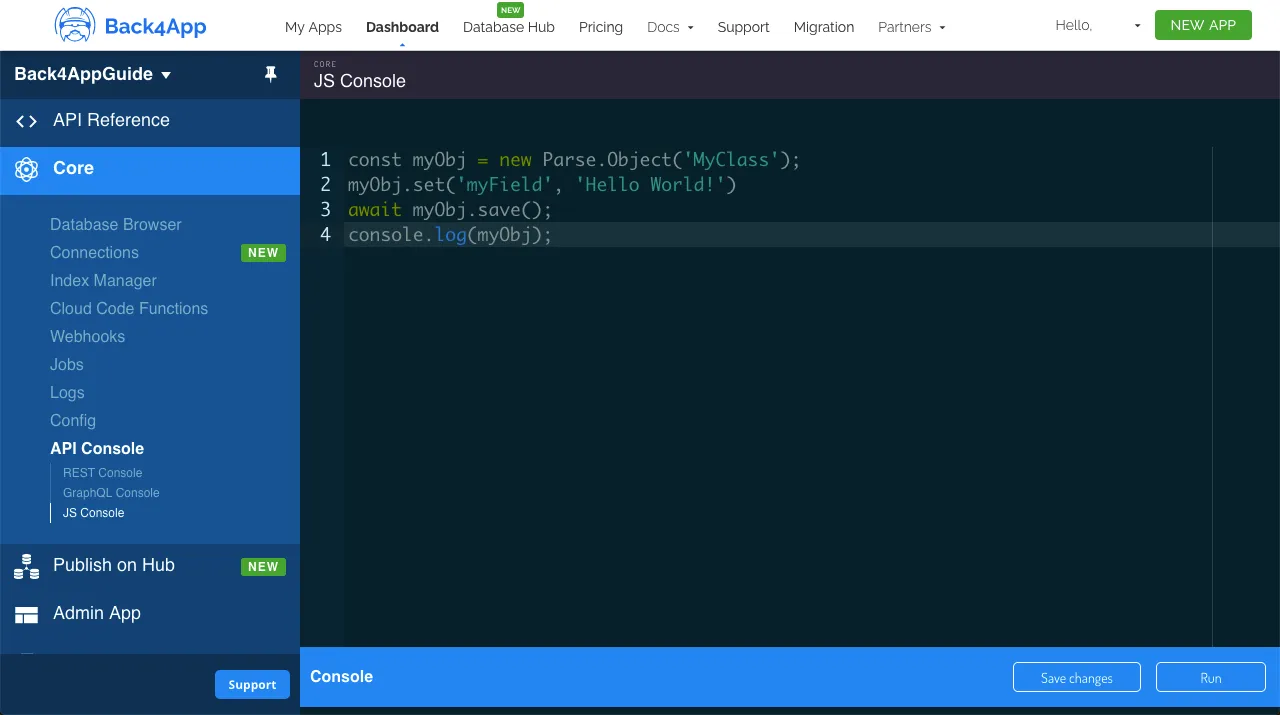
On Parse JS Console is possible to run JavaScript code directly, querying and updating your application database contents using the JS SDK commands. Run the code below from your JS Console and insert the data on Back4App. Here is how the JS console looks like in your dashboard:
Go ahead and create the classes with the following example content:
Now that you have populated all the classes, we can now perform some relational queries in it. Let’s begin by filtering Book results by the publisher, searching for the ones that belong to the Publisher “Acacia Publishings” (or “Publisher A”) using the basic Parse.Query.equalTo method:
Let’s now query which BookStore objects contain Book objects with publishing date greater than 01/01/2010, using an inner query with the Parse.Query.greaterThan method and then the Parse.Query.matchesQuery method:
Let’s now create a more complex relational query, looking for BookStore objects that have at least one Book written by Author “Aaron Writer” (or “AuthorA”), using equalTo and matchesQuery:
Let’s now use our example queries inside a component in React Native, with a simple interface having a list showing results and also buttons for calling the queries. This is how the component code is laid out, note the doQuery functions, containing the example code from before.
This is how the component should look like after rendering and querying by one of the query functions:
At the end of this guide, you learned how relational queries work on Parse and how to perform them on Back4App from a React Native App. In the next guide, you will learn how to work with Users in Parse.