How to Develop a CRUD Application with Flask?
This tutorial will guide you through building a CRUD (create, read, update, delete) application using Flask.
We'll integrate Back4app as our backend service to simplify data management. You will learn to set up a Back4app project, design a flexible data structure, and implement CRUD functionalities using Flask.
In this walkthrough, you'll first create a Back4app project named Basic-CRUD-App-Flask that offers a robust, non-relational data storage solution.
You'll define your data schema with classes and fields either manually or using Back4app’s AI Agent.
After configuring your backend with Back4app’s Admin interface, you will connect your Flask application to the service via REST API calls. This tutorial also covers secure access management for your data.
By the end, you will have a production-ready Flask application capable of performing CRUD operations along with secure user authentication and data handling.
- How to create a Flask-based CRUD app with a non-relational backend.
- How to structure your backend on Back4app and integrate it with a Flask project.
- How to utilize the Back4app Admin interface to manage CRUD operations effortlessly.
- How to deploy your Flask application, including using Docker for containerization.
Before you begin, ensure you have:
- A Python development environment set up. Use an editor like VSCode or PyCharm and install Python 3.8 (or later).
- Log in to your Back4app account.
- Click on “New App” from your dashboard.
- Enter the project name: Basic-CRUD-App-Flask and complete the setup process.
After creation, your project appears on the dashboard, serving as the base for your backend configuration.
For this application, you'll establish several classes in your Back4app project. Below are examples of the core classes and their fields essential for CRUD operations.
Field | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
_id | ObjectId | Auto-generated unique identifier. |
title | String | The name or title of the item. |
description | String | A brief overview of the item. |
createdAt | Date | Timestamp when the item was created. |
updatedAt | Date | Timestamp for the latest update. |
Field | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
_id | ObjectId | Auto-generated unique identifier. |
username | String | Unique username for the user. |
String | Unique email address. | |
passwordHash | String | Securely hashed password for authentication. |
createdAt | Date | Timestamp when the user account was created. |
updatedAt | Date | Timestamp for the last account update. |
You can create these classes and add fields directly in your Back4app dashboard.
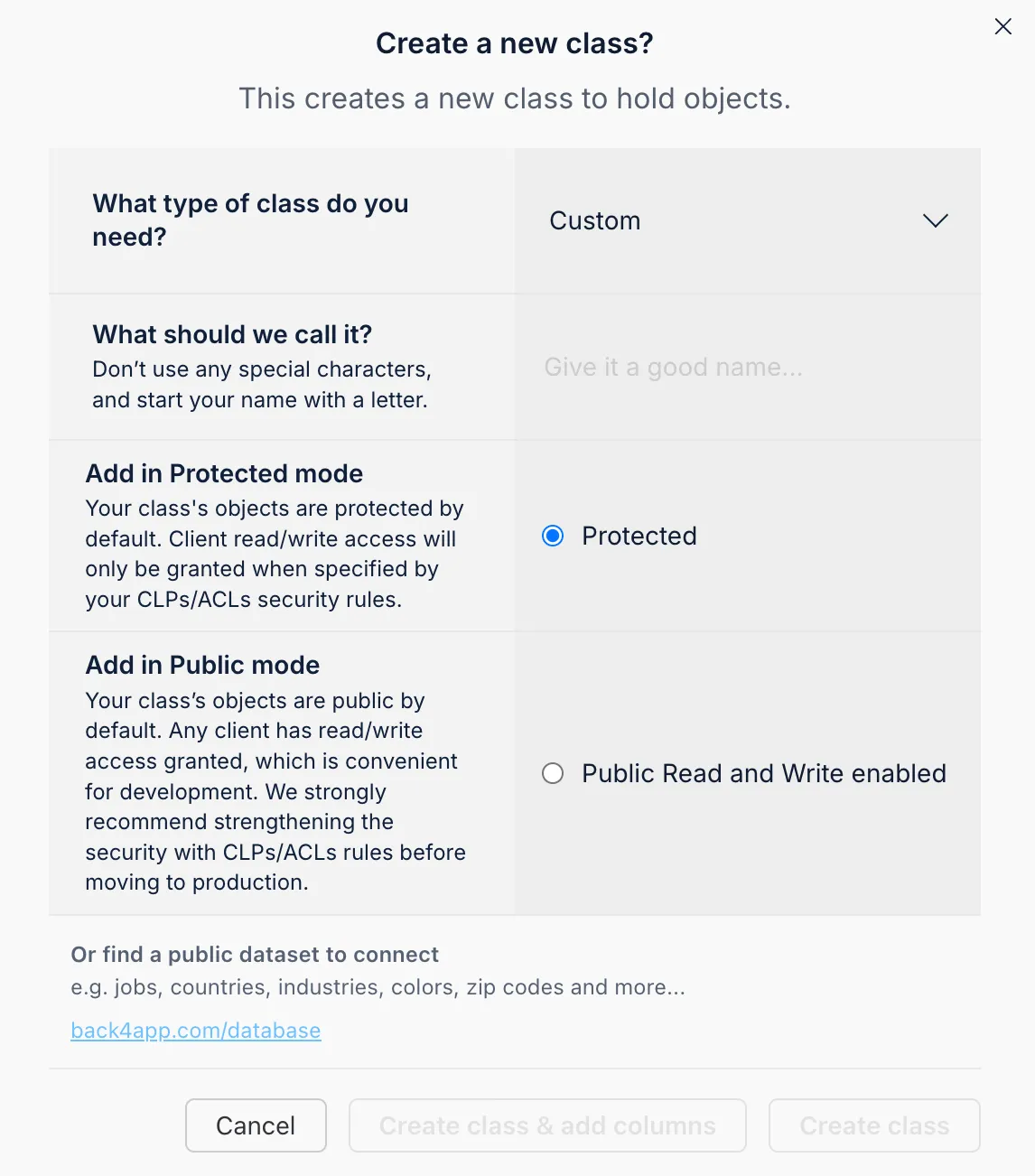
You can add columns by choosing a data type, naming the field, setting default values, and marking it as required.
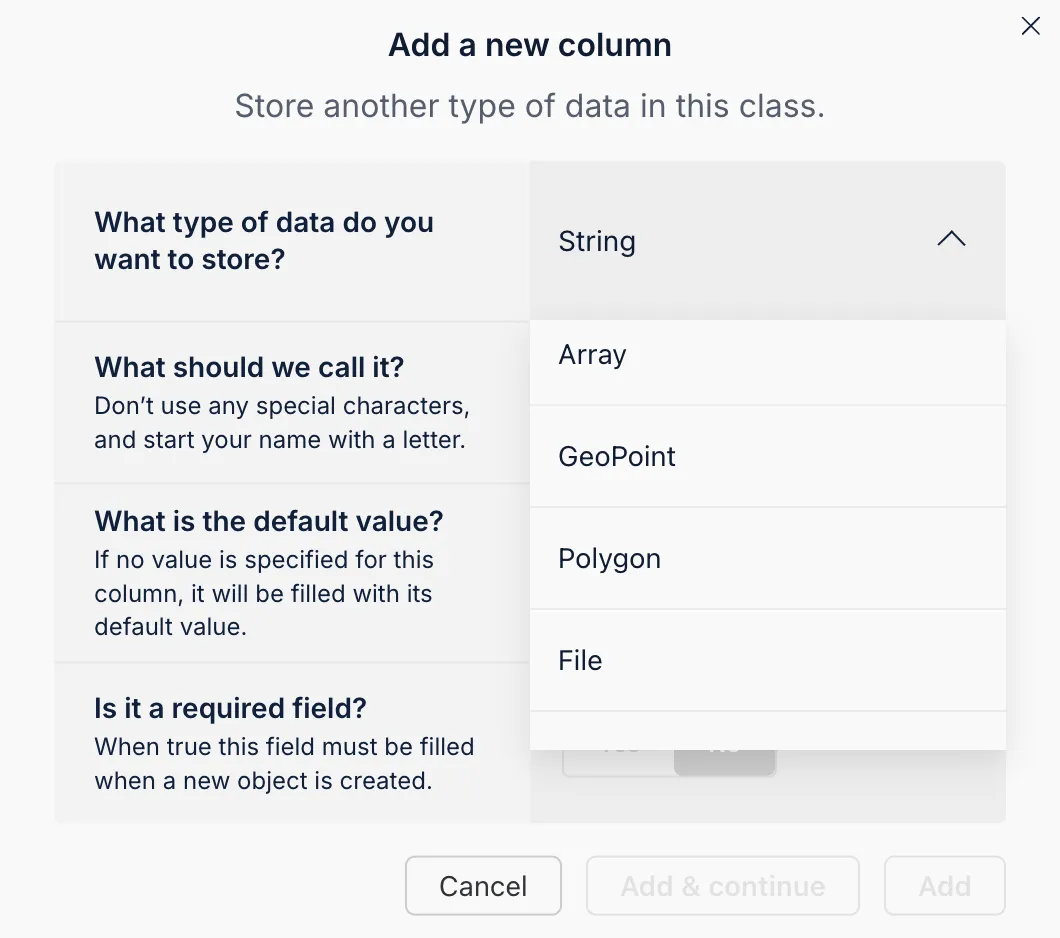
The AI Agent in your dashboard can automatically establish the schema based on your instructions. This tool simplifies the process and ensures your data model is optimal for CRUD tasks.
- Open the AI Agent: Sign in to your Back4app dashboard and locate the AI Agent under project settings.
- Describe Your Schema: Provide a detailed prompt listing the classes and fields.
- Confirm the Setup: Review the proposed schema and approve the changes.
This AI-driven process saves time and guarantees a consistent, effective data model.
Back4app’s Admin interface provides a no-code solution to manage your backend data. With its drag and drop features, you can easily perform CRUD operations—such as adding, editing, or deleting records.
- Go to the “More” menu on your Back4app dashboard.
- Select “Admin App” and click “Enable Admin App.”
- Create your admin account, which also sets up initial roles like B4aAdminUser.
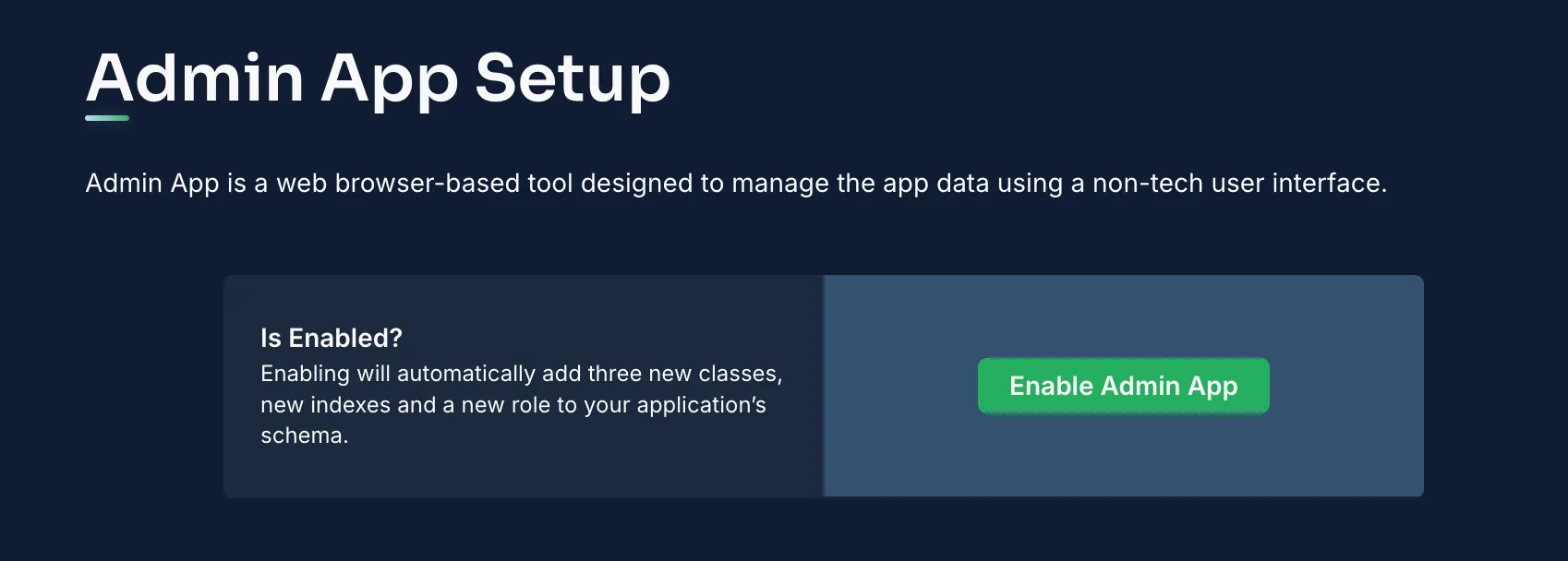
After activation, sign in to the Admin interface to manage your project data.
Within the Admin interface, you can:
- Insert New Entries: Click “Add Record” within a class (e.g., Items) to create new data.
- View and Modify Entries: Select any record to see details or update fields.
- Delete Records: Remove entries that are no longer required.
This easy-to-use interface improves productivity by streamlining backend management.
With your backend set up, the next step is to link your Flask application to Back4app.
Since there isn’t a dedicated Parse SDK for Flask, you will use REST API calls. In your Flask app, you can utilize the requests library to perform CRUD operations.
Install the Requests Library: Run the following command in your terminal:
Bash1pip install requestsConfigure a Python Module for API Calls: Create a file called back4app_api.py:
Python1# back4app_api.py 2import requests 3 4APPLICATION_ID = "YOUR_APPLICATION_ID" 5REST_API_KEY = "YOUR_REST_API_KEY" 6BASE_URL = "https://parseapi.back4app.com/classes" 7 8HEADERS = { 9 "X-Parse-Application-Id": APPLICATION_ID, 10 "X-Parse-REST-API-Key": REST_API_KEY, 11 "Content-Type": "application/json" 12} 13 14def get_items(): 15 response = requests.get(f"{BASE_URL}/Items", headers=HEADERS) 16 return response.json() 17 18def create_item(title, description): 19 data = {"title": title, "description": description} 20 response = requests.post(f"{BASE_URL}/Items", headers=HEADERS, json=data) 21 return response.json() 22 23def update_item(object_id, title, description): 24 data = {"title": title, "description": description} 25 response = requests.put(f"{BASE_URL}/Items/{object_id}", headers=HEADERS, json=data) 26 return response.json() 27 28def delete_item(object_id): 29 response = requests.delete(f"{BASE_URL}/Items/{object_id}", headers=HEADERS) 30 return response.json()Integrate API Functions in Your Flask Routes: For example, in app.py:
Python1# app.py 2from flask import Flask, request, jsonify, render_template 3from back4app_api import get_items, create_item, update_item, delete_item 4 5app = Flask(__name__) 6 7@app.route("/") 8def index(): 9 items = get_items() 10 return render_template("index.html", items=items.get("results", [])) 11 12@app.route("/add", methods=["POST"]) 13def add_item(): 14 title = request.form.get("title") 15 description = request.form.get("description") 16 result = create_item(title, description) 17 return jsonify(result) 18 19@app.route("/update/<item_id>", methods=["PUT"]) 20def modify_item(item_id): 21 data = request.get_json() 22 result = update_item(item_id, data.get("title"), data.get("description")) 23 return jsonify(result) 24 25@app.route("/delete/<item_id>", methods=["DELETE"]) 26def remove_item(item_id): 27 result = delete_item(item_id) 28 return jsonify(result) 29 30if __name__ == "__main__": 31 app.run(debug=True)
This example illustrates how to use REST calls within Flask to interact with your Back4app backend.
Safeguard your data by configuring access controls. For instance, when creating a new item, you might restrict access to its creator.
Below is an example using API calls with controlled access:
Adjust the Class-Level Permissions (CLPs) directly in the Back4app dashboard to ensure only authenticated users can access specific classes.
Back4app offers built-in user management via its Users class. In your Flask app, you can create endpoints for registration and login.
You can create corresponding Flask routes to handle user registration and login using these functions.
Back4app simplifies deployment. You can deploy your Flask app via several methods, including Docker.
- Prepare Your Application: Ensure all required files and dependencies are included.
Test Locally: Run your app locally with:
Bash1flask run
A typical structure might be:
Include a Dockerfile at the project root:
- Connect Your GitHub Repository: Ensure your code is pushed to GitHub.
- Configure Deployment Settings: In the Back4app dashboard, use the Web Deployment feature to link your repository (e.g., Basic-CRUD-App-Flask) and select your branch.
- Define Build Commands: Specify the build command (e.g., pip install -r requirements.txt) and the location of your application.
- Deploy: Click Deploy and monitor the logs until your application is live.
Great job! You have successfully created a Flask-based CRUD application integrated with Back4app.
You established a project named Basic-CRUD-App-Flask, defined data models for Items and Users, and managed your backend via the Back4app Admin interface.
Additionally, you connected your Flask application using REST API calls and implemented security measures.
What’s Next?
- Expand Functionality: Consider adding features like advanced search, detailed item views, or real-time updates.
- Enhance Backend Services: Explore cloud functions, integrate third-party APIs, or implement role-based access control.
- Deepen Your Skills: Visit the Back4app documentation and other resources to further refine your application.
Happy coding and best of luck with your Flask CRUD application!
