How to Develop a CRUD Android Application Using Java?
In this tutorial, you will learn how to build a fully functional CRUD (create, read, update, delete) application for Android using Java.
We will use Back4app as our backend to easily manage data. This guide will walk you through setting up a Back4app project, designing your data schema, and coding CRUD functionalities in an Android environment.
Initially, you will establish a Back4app project titled Basic-CRUD-App-Android that provides a reliable backend solution. You’ll then define your data structures by creating the necessary classes and fields manually or by leveraging Back4app’s AI-driven schema generator.
Next, you’ll explore the Back4app Admin App—a user-friendly, drag-and-drop interface that simplifies data management.
Finally, you will connect your Android app to Back4app using the Parse Android SDK, enabling secure CRUD operations and user authentication.
By the end of this guide, you will have developed a production-ready Android application that handles essential CRUD operations along with secure user management.
- Build an Android CRUD application integrated with a robust backend.
- Understand how to structure a scalable backend and connect it with your Android app.
- Utilize Back4app’s Admin App to effortlessly manage create, read, update, and delete operations.
- Learn secure data handling and user authentication in an Android context.
Before you begin, ensure you have:
- An Android development setup. Use Android Studio with Java support and ensure you have at least Android API 21.
- Basic knowledge of Java, Android app development, and RESTful APIs. Review the Android documentation if needed.
- Log into your Back4app account.
- Select “New App” from your dashboard.
- Name your project: Basic-CRUD-App-Android and follow the instructions to complete the setup.
After your project is set up, it will appear on your dashboard, ready for further configuration.
For this Android CRUD application, you need to create several classes (collections) within your Back4app project. The examples below illustrate the main classes and their essential fields for supporting CRUD functionality.
This collection stores details about each item.
Field | Data Type | Purpose |
|---|---|---|
_id | ObjectId | System-generated unique identifier. |
title | String | Name or title of the item. |
description | String | Brief overview of the item. |
createdAt | Date | Timestamp when the item was added. |
updatedAt | Date | Timestamp for the latest update. |
This collection handles user credentials and authentication details.
Field | Data Type | Purpose |
|---|---|---|
_id | ObjectId | Automatically assigned unique ID. |
username | String | Unique username for the user. |
String | Unique email address. | |
passwordHash | String | Securely stored password. |
createdAt | Date | Account creation timestamp. |
updatedAt | Date | Timestamp for account updates. |
You can create these collections and their fields directly from the Back4app dashboard.
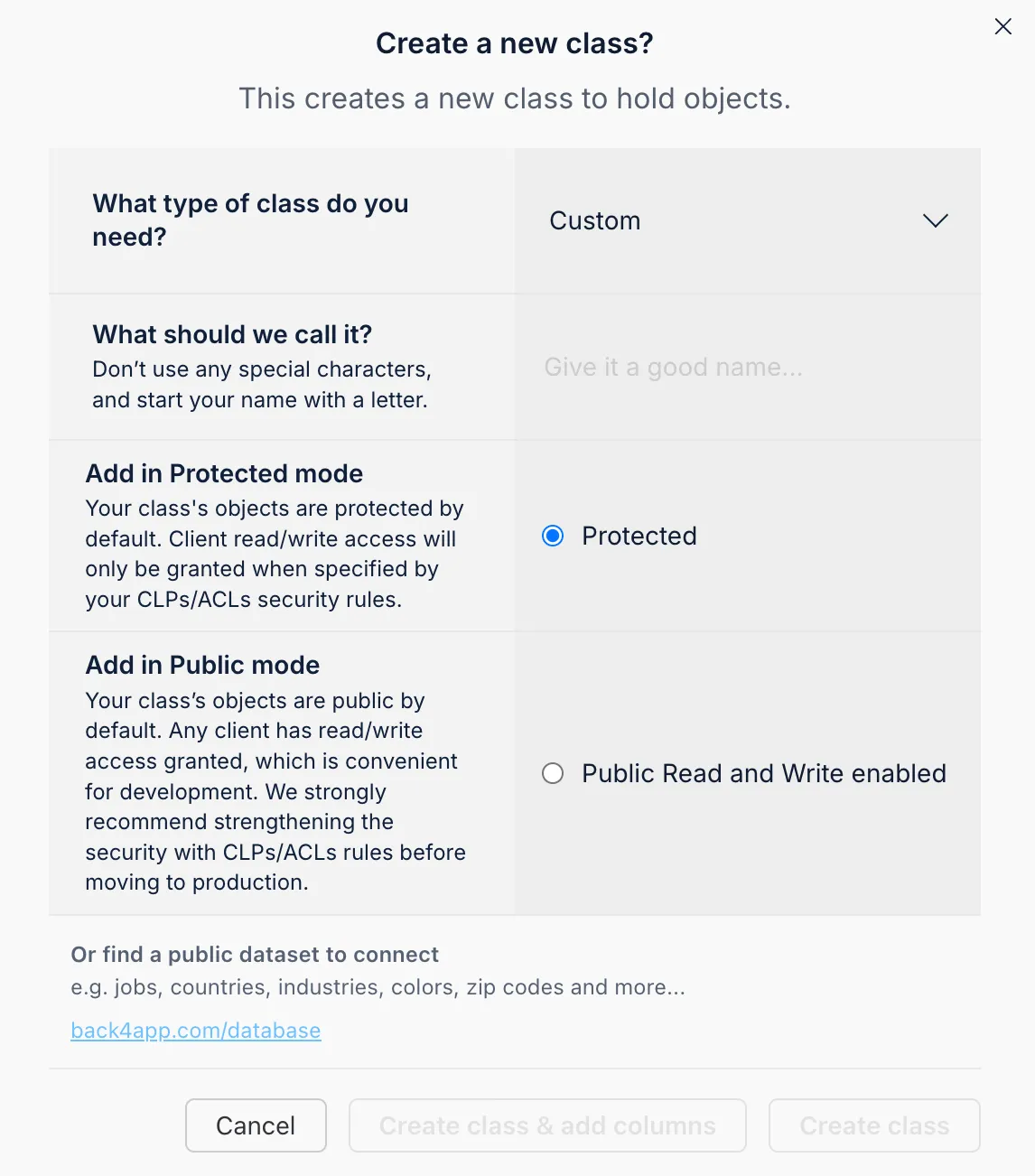
To add a new field, simply select the desired data type, enter the field name, set a default value if needed, and indicate whether it is required.
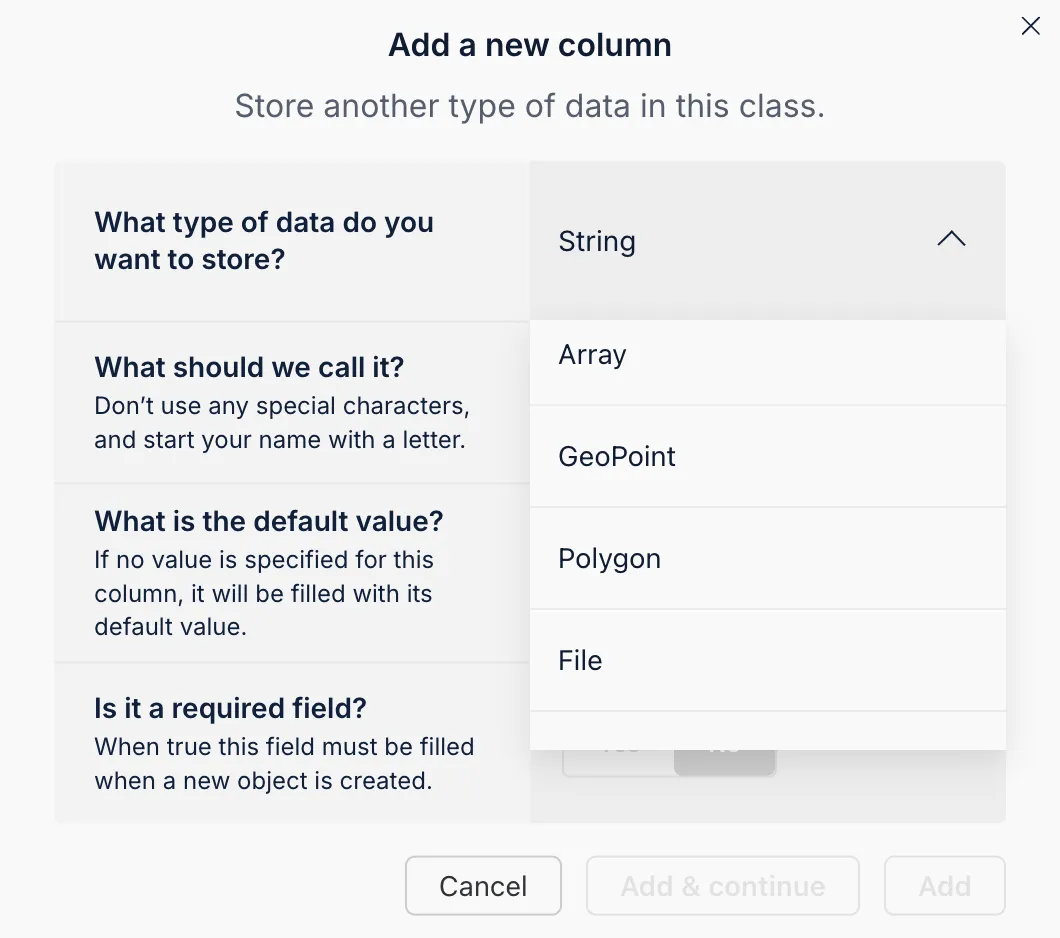
The integrated Back4app AI Assistant can automatically generate your schema from a brief description, expediting your project setup.
- Access the AI Assistant: In your Back4app dashboard, find the AI Assistant under the project settings.
- Describe Your Schema: Enter a detailed description of the collections and fields you need.
- Review and Confirm: The AI Assistant will propose a schema. Review the details and confirm to implement the changes.
This AI-assisted method saves time and ensures your data schema is optimized for CRUD operations.
The Back4app Admin Console provides a visual interface for managing your backend data without writing any code. Its drag-and-drop features make it easy to execute CRUD operations such as adding, modifying, and removing records.
- Open the “More” menu in your Back4app dashboard.
- Choose “Admin App” and then click “Enable Admin App.”
- Create your admin credentials by setting up your primary admin account. This process will also create system roles (like B4aAdminUser) and system classes.
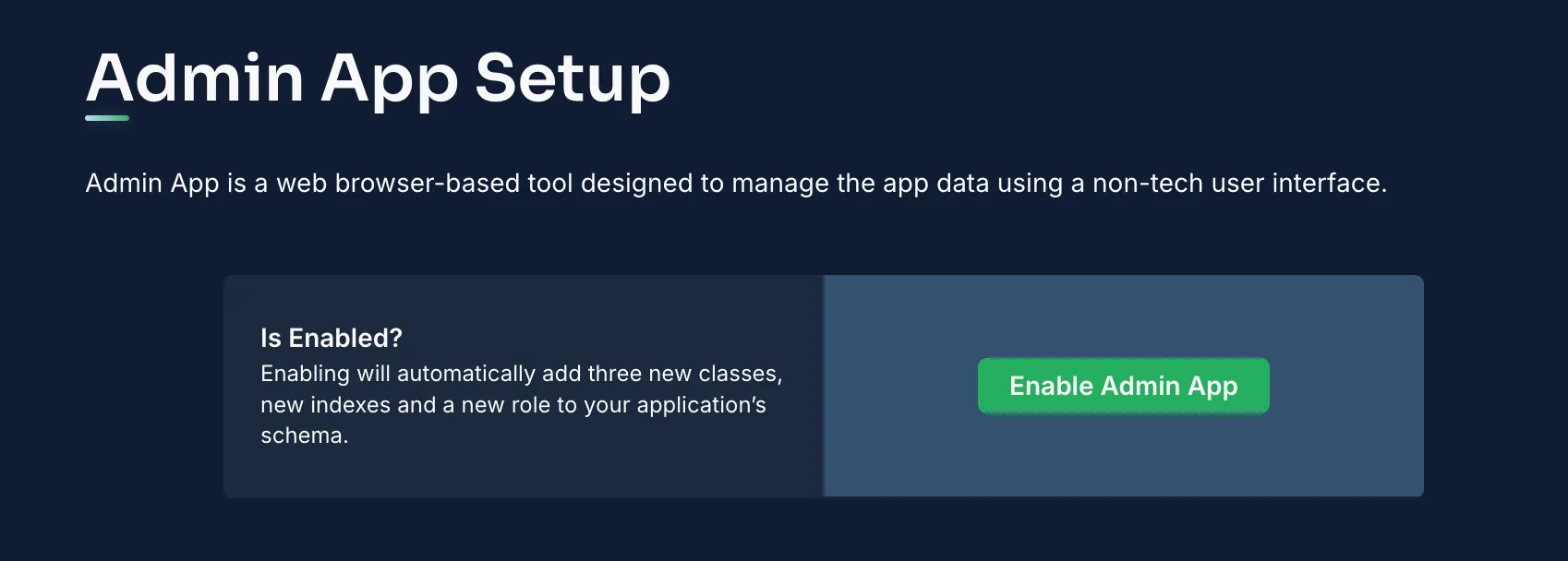
Once activated, sign in to the Admin Console to manage your data.
Within the Admin Console you can:
- Add New Records: Utilize the “Add Record” button in a collection (for example, Items) to insert new data.
- View and Edit Records: Click on any entry to review or update its details.
- Delete Records: Remove entries that are no longer needed.
This interface greatly simplifies the process of backend data management.
With your backend prepared, the next step is to link your Android application to Back4app.
Include the Parse Android SDK in Your Project: Add the following dependency in your build.gradle file:
Initialize Parse in Your Application Class: Create an initializer (e.g., ParseInitializer.java):
Implementing CRUD Operations in Your Android App: For example, create a service class to manage item data:
If the Parse Android SDK isn’t suitable, you can execute CRUD tasks through REST calls. For instance, to retrieve items via REST:
Integrate these API calls within your Android classes as required.
Ensure your data remains protected by configuring ACLs for your objects. For instance, to create an item that is only accessible to its owner:
In the Back4app dashboard, adjust the CLPs for your collections to ensure that only authenticated users can access sensitive data.
Back4app uses Parse’s built-in User collection for managing authentication. In your Android app, implement registration and login as follows:
You can also implement additional features such as session management and password resets as needed.
Great job! You’ve successfully created a basic CRUD Android application using Java and integrated it with Back4app.
In this tutorial, you set up a project called Basic-CRUD-App-Android, defined collections for Items and Users, and managed your data via the Back4app Admin Console.
Moreover, you connected your Android app using the Parse Android SDK (or REST/GraphQL as an alternative) and implemented strong security measures.
Next Steps:
- Expand Your Application: Add new features like advanced search, detailed item views, or real-time notifications.
- Enhance Backend Functionality: Experiment with cloud functions, integrate third-party APIs, or set up role-based access.
Happy coding and enjoy building your Android CRUD application!
