How to Create a CRUD Application with Ember.js?
In this walkthrough, you'll learn how to build a simple CRUD (create, read, update, delete) application using Ember.js.
We'll rely on Back4app as the backend service to effortlessly manage your data. This guide covers all the basic operations of a CRUD system, showing you how to set up a Back4app project, design a dynamic data model, and integrate CRUD operations into an Ember.js application.
At the outset, you'll establish a Back4app project named Basic-CRUD-App-Ember which supplies a reliable non-relational data storage solution for your app. You'll define your data structure by setting up models and fields either manually or with the help of Back4app's AI Agent.
Next, you'll explore the Back4app Admin App—a no-code interface that lets you manage data with simple drag and drop interactions. Finally, you'll integrate your Ember.js app with Back4app via API calls, implementing secure access controls along the way.
By the end of this tutorial, you'll have a production-ready Ember.js application capable of performing all CRUD operations, including secure user authentication and effective data management.
- Build an Ember.js-based CRUD application backed by a robust backend platform.
- Understand how to structure and integrate a scalable backend with an Ember.js front end.
- Use Back4app’s intuitive Admin App to effortlessly perform create, read, update, and delete operations.
- Learn about deployment strategies, including Docker containerization, for seamless application delivery.
Before diving in, please confirm you have:
- An Ember.js development setup. Install Ember CLI and set up your environment by following Ember.js guides.
- Basic familiarity with Ember.js, JavaScript, and REST APIs. Brush up on these topics if needed.
- Log in to your Back4app account.
- Click on the “New App” button from your dashboard.
- Assign the project name: Basic-CRUD-App-Ember and follow the subsequent prompts to complete the project setup.
Once the project is created, it will appear in your dashboard and form the foundation for your backend configuration.
For this CRUD application, you'll define several models in your Back4app project. Below are examples outlining the core models and their fields necessary for performing CRUD operations.
This model stores information about each item.
Field | Data Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
_id | ObjectId | Auto-generated unique identifier. |
title | String | Name of the item. |
description | String | Brief summary of the item. |
createdAt | Date | Timestamp marking when the item was added. |
updatedAt | Date | Timestamp marking the last update. |
This model handles user authentication and credentials.
Field | Data Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
_id | ObjectId | Auto-generated unique identifier. |
username | String | Unique username for the user. |
String | User's unique email address. | |
passwordHash | String | Encrypted user password. |
createdAt | Date | Timestamp when the account was created. |
updatedAt | Date | Timestamp when the account was updated. |
You can create these models and define their fields directly within the Back4app dashboard.
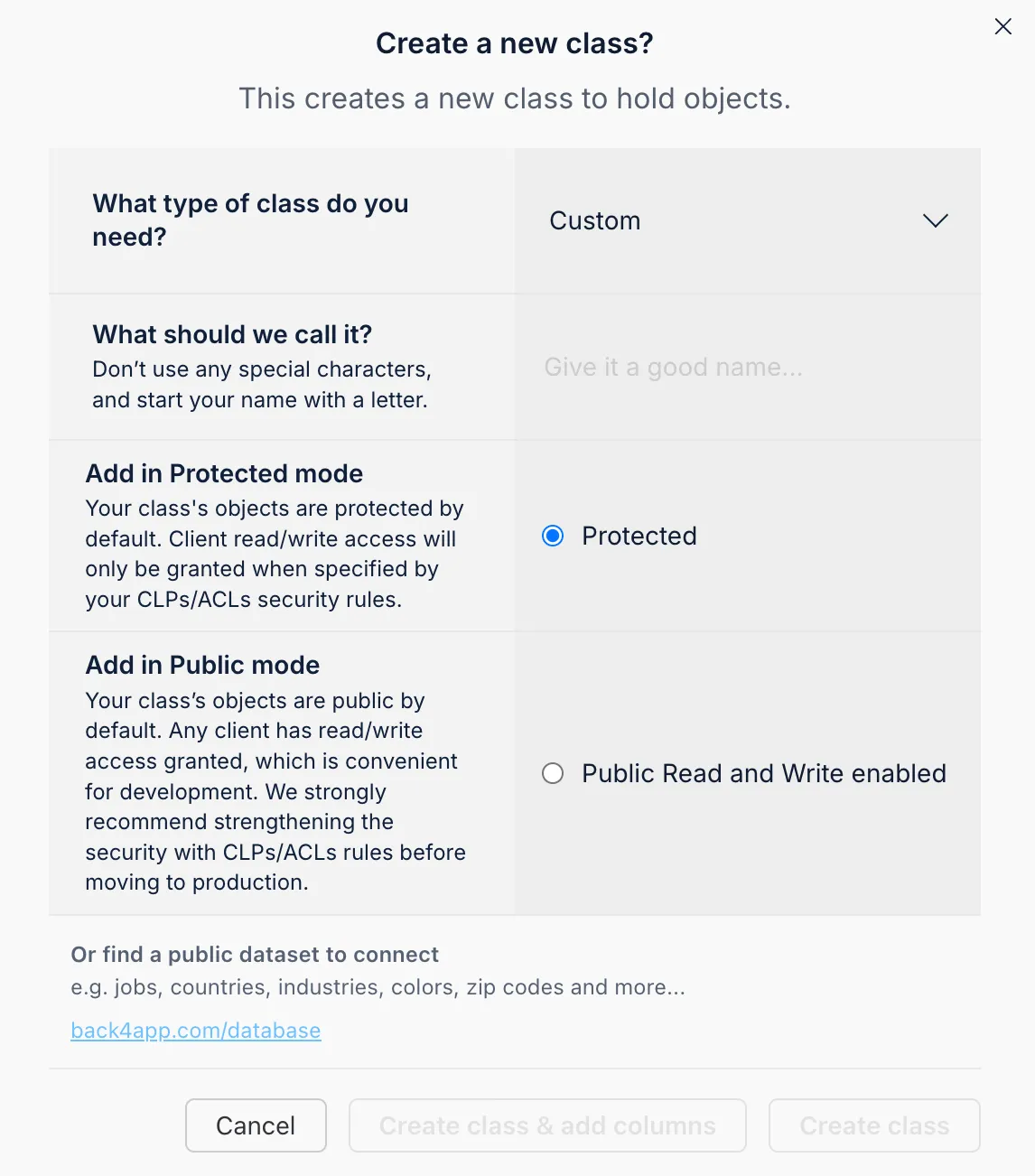
You can add fields by selecting a data type, entering the field name, setting a default value, and marking whether it is mandatory.
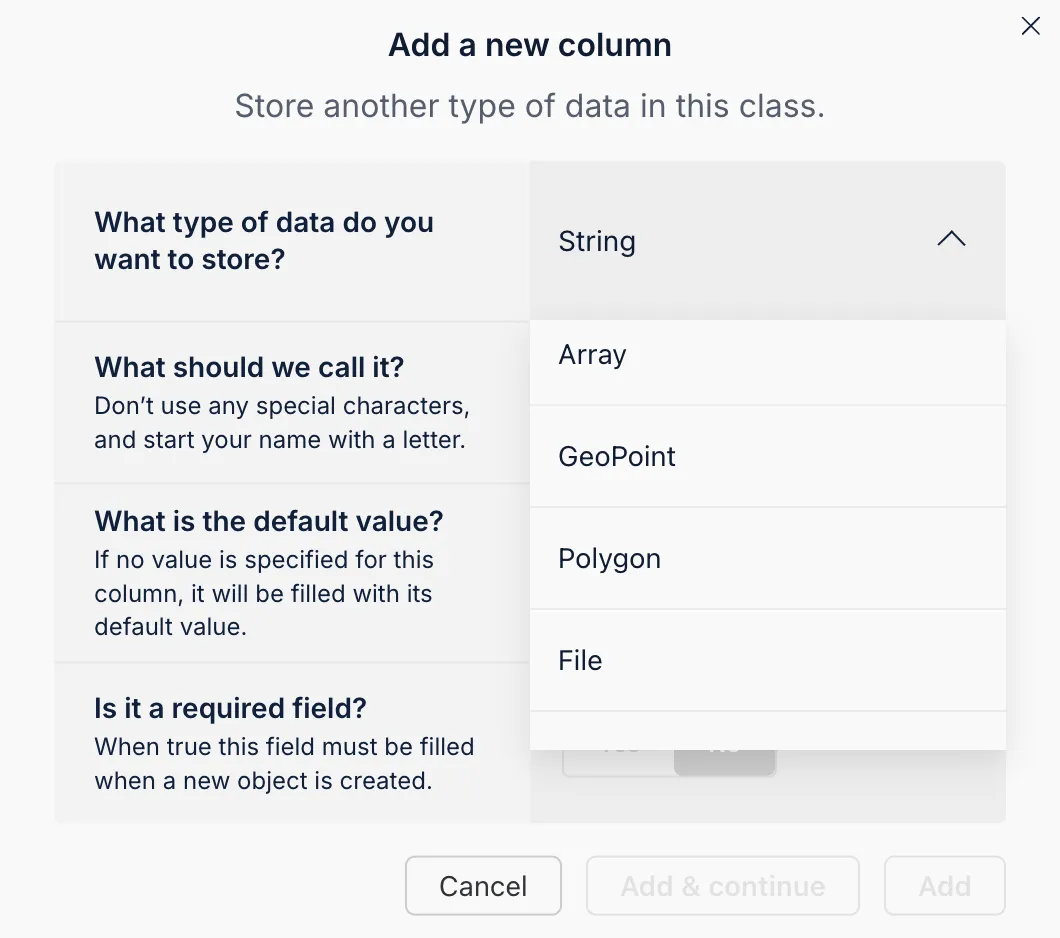
The Back4app AI Agent is an intelligent feature within your dashboard that can automatically configure your data schema based on your specifications. This tool simplifies project initialization by ensuring your data model is optimized for CRUD operations.
- Open the AI Agent: Log into your Back4app dashboard and find the AI Agent in the project settings.
- Provide Your Model Details: Submit a detailed description of the models and fields you need.
- Review and Confirm: The AI Agent will generate a suggested schema. Confirm the details to apply the configuration.
This AI-assisted approach saves time and ensures your data structure is consistent and optimized.
The Back4app Admin App provides a user-friendly, no-code platform for managing your backend data. Its drag and drop interface allows you to easily perform CRUD tasks such as adding, viewing, updating, and removing records.
- Go to the “More” menu in your Back4app dashboard.
- Select “Admin App” and click on “Enable Admin App.”
- Configure your admin credentials by creating an initial admin account. This will also set up roles (e.g., B4aAdminUser) and system models.
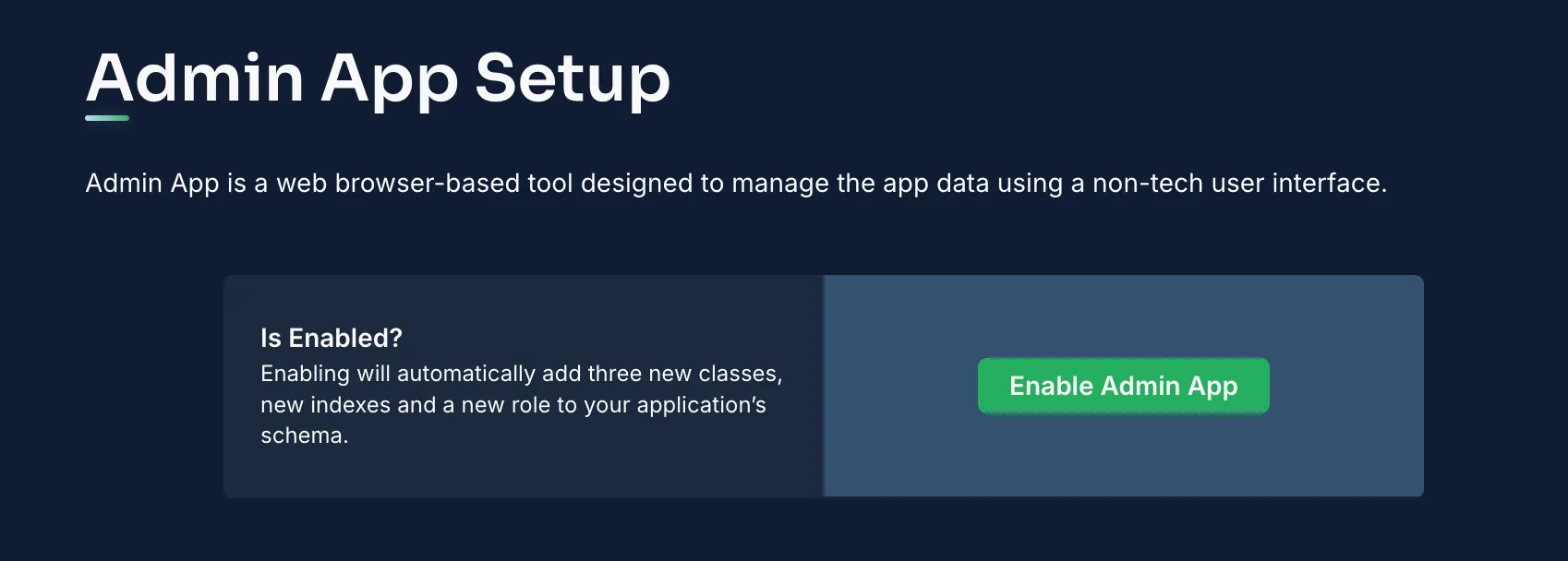
Once activated, log into the Admin App to manage your application's data.
Inside the Admin App, you can:
- Insert Records: Click the “Add Record” button within a model (e.g., Items) to input new data.
- Inspect/Modify Records: Select any record to view its details or edit its fields.
- Delete Records: Remove entries that are no longer needed.
This streamlined interface significantly improves the efficiency of data management.
With your backend configured, it’s time to connect your Ember.js application to Back4app.
Ember.js leverages Ember Data for handling data operations. In this tutorial, you will use the REST adapter to interact with your Back4app backend.
Create or update your application's adapter (e.g., app/adapters/application.js) with the following configuration:
Create an Ember model for item (e.g., app/models/item.js):
And similarly for user (e.g., app/models/user.js):
Use Ember Data’s store service to perform CRUD operations. For example, to fetch all items, you might create a route similar to:
You can similarly add, update, or delete records using Ember Data’s API methods.
If you prefer not to use Ember Data, you can utilize native fetch calls. For example, to retrieve items:
Integrate these API calls into your Ember components or services as needed.
Safeguard your data by configuring Access Control Lists (ACLs) for each object. For example, when creating an item that should be visible only to its owner, you can adjust the ACL settings via your API calls.
Within the Back4app dashboard, set up CLPs to ensure that only authenticated users have access to certain models. This adds an extra layer of security by enforcing default access rules.
Back4app leverages the Parse User model for handling authentication. In your Ember.js application, you can create services to manage user sign-up and login via API calls.
For example, create an authentication service (app/services/auth.js):
This service can be injected into your routes or components to handle session management, password resets, and other authentication-related tasks.
Back4app supports various deployment strategies. You can deploy your Ember.js application using methods like Docker containerization.
Build Your Application: Run the following command in your terminal:
- Verify the Output: Ensure the dist/ folder contains your production-ready assets.
A typical Ember.js project might be organized as follows:
If you prefer a containerized deployment, include a Dockerfile in your project root:
- Connect Your GitHub Repository: Host your Ember.js project on GitHub.
- Configure Deployment Settings: In your Back4app dashboard, navigate to Web Deployment, link your repository (e.g., Basic-CRUD-App-Ember), and select the desired branch.
- Set Build Commands: Define your build command (e.g., ember build --environment=production) and specify the output directory.
- Deploy Your App: Click Deploy and monitor the logs until your app goes live.
Great job! You’ve now built an Ember.js-based CRUD application integrated with Back4app.
In this tutorial, you set up a project called Basic-CRUD-App-Ember, designed models for Items and Users, and managed your backend via the Back4app Admin App.
You also connected your Ember.js app using API calls and implemented robust security practices.
Next Steps:
- Enhance Your Application: Consider adding features such as advanced search functionality, detailed views, or live updates.
- Expand Backend Capabilities: Explore cloud functions, integrate third-party APIs, or set up role-based access control.
- Deepen Your Understanding: Visit the Back4app documentation and other Ember.js resources for more advanced topics.
Happy coding and best wishes on your journey with Ember.js!
