How to Develop a CRUD Application with Deno? A Comprehensive Guide
This guide demonstrates how to create a simple CRUD (create, read, update, delete) application using Deno.
We will leverage Back4app as our backend management platform, configuring it to operate as a reliable database solution and we will employ the API approach to interact with our backend services.
In this tutorial, you will:
- Set up a Back4app project called Basic-CRUD-App-Deno.
- Design and configure your database schema with collections and fields tailored for CRUD operations.
- Utilize the Back4app Admin App to manage your collections via an intuitive, drag-and-drop interface.
- Connect your Deno frontend with Back4app using REST/GraphQL calls.
- Secure your backend with robust access control measures.
By the end of this guide, you will have built a production-ready web application that supports essential data operations and user authentication.
- Master CRUD functionalities to efficiently handle data.
- Learn how to design a scalable backend integrated with a Deno-based frontend.
- Use the Back4app Admin App for seamless data management.
- Discover deployment strategies, including containerization with Docker.
Before starting, please ensure you have:
- A Deno development setup. Make sure Deno is installed and updated (version 1.10+ is recommended).
- Familiarity with JavaScript/TypeScript, Deno, and REST API concepts. Consult the Deno Manual for further reading.
- Log into your Back4app account.
- Click the “New App” button on your dashboard.
- Name your project: Basic-CRUD-App-Deno and follow the on-screen instructions.
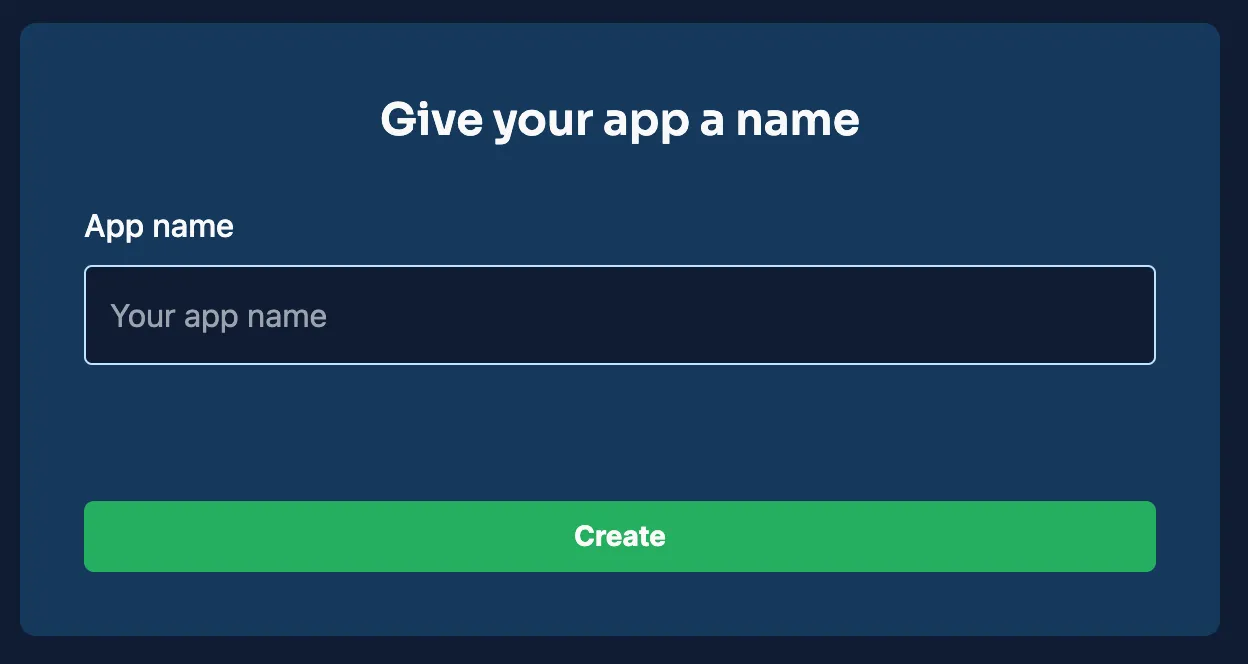
After the project is created, it will be visible on your dashboard, laying the groundwork for your backend configuration.
For this CRUD application, you will define multiple collections. Below are sample collections with suggested fields to facilitate basic operations.
This collection holds details for each item.
Field | Type | Purpose |
|---|---|---|
_id | ObjectId | Auto-generated primary key. |
title | String | Name of the item. |
description | String | Brief summary of the item. |
created_at | Date | Timestamp for when the item was added. |
updated_at | Date | Timestamp for the latest update. |
This collection stores user profiles and authentication data.
Field | Type | Purpose |
|---|---|---|
_id | ObjectId | Auto-generated primary key. |
username | String | Unique identifier for the user. |
String | User's unique email address. | |
password_hash | String | Securely hashed password. |
created_at | Date | Account creation timestamp. |
updated_at | Date | Last updated timestamp. |
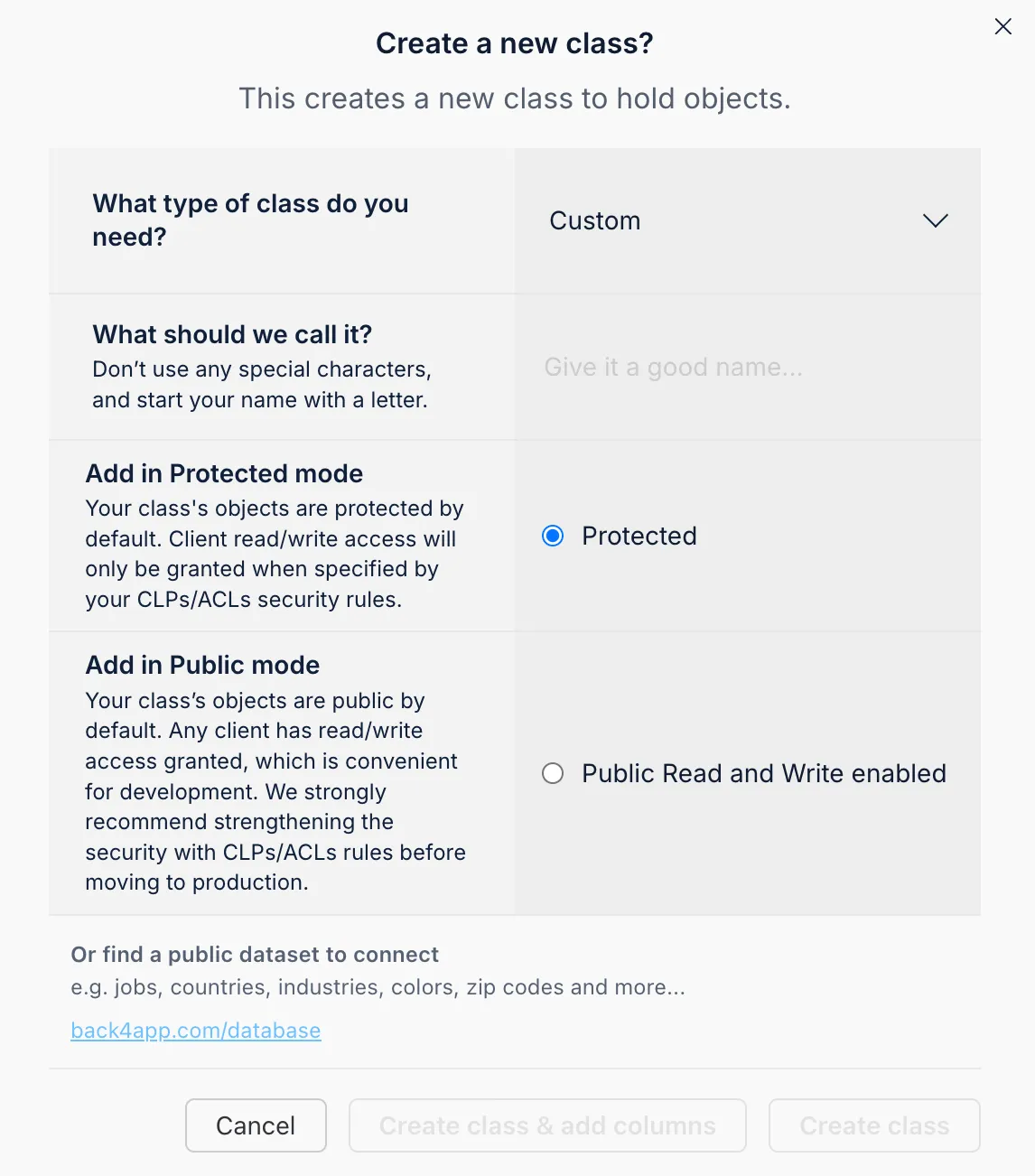
You can manually create these collections in the Back4app dashboard by establishing a new class for each and adding columns to define each field.
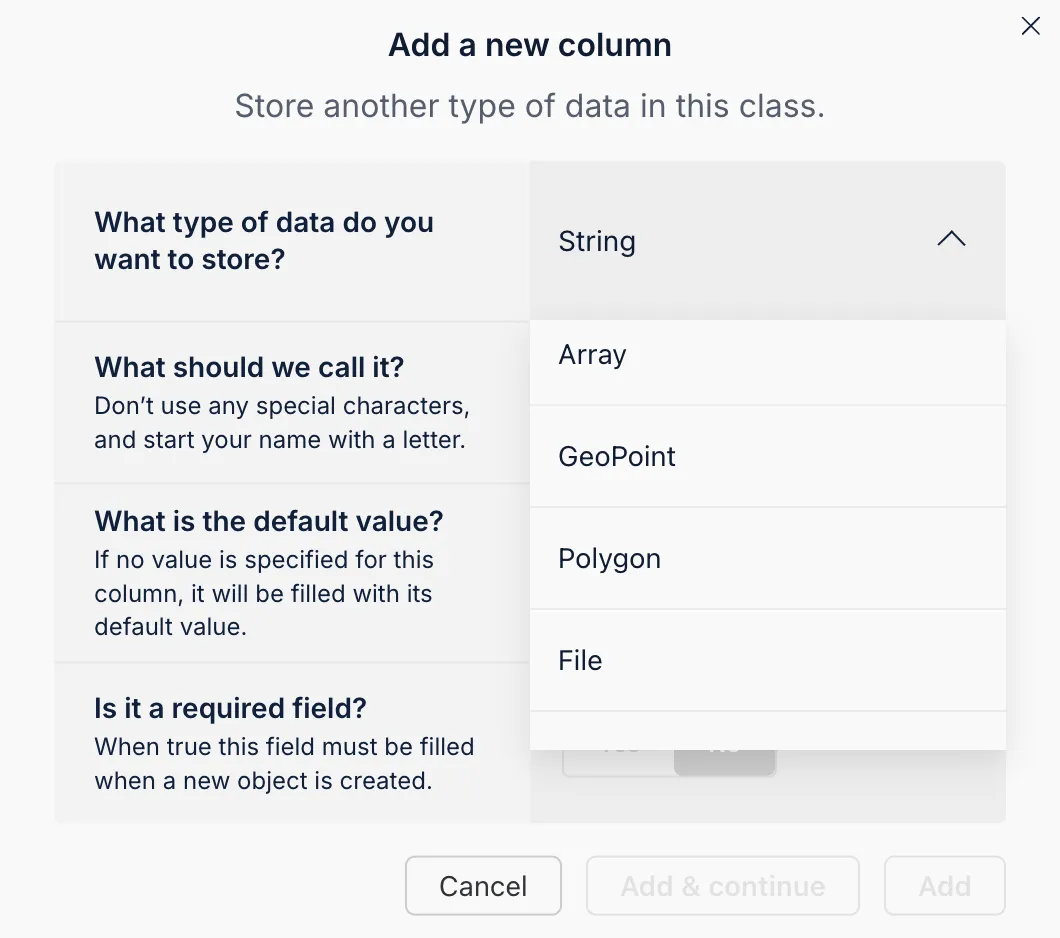
You can also add fields by selecting their type, naming them, setting defaults, and marking them as required.
The Back4app AI Agent simplifies schema generation by allowing you to input a descriptive prompt, which then automatically creates the required collections and fields.
- Access the AI Agent: Open your Back4app dashboard and locate the AI Agent option.
- Input Your Data Model Description: Provide a detailed prompt listing your collections and fields.
- Review and Apply: Inspect the generated schema suggestions and implement them in your project.
This approach ensures consistency and efficiency in setting up your backend schema.
The Back4app Admin App offers a no-code interface to handle your backend data. Its intuitive drag-and-drop design facilitates easy management of CRUD operations.
- Go to the “More” menu on your Back4app dashboard.
- Select “Admin App” and click on “Enable Admin App.”
- Set up your admin credentials by creating an initial admin user, which also configures roles (e.g., B4aAdminUser) and system collections.
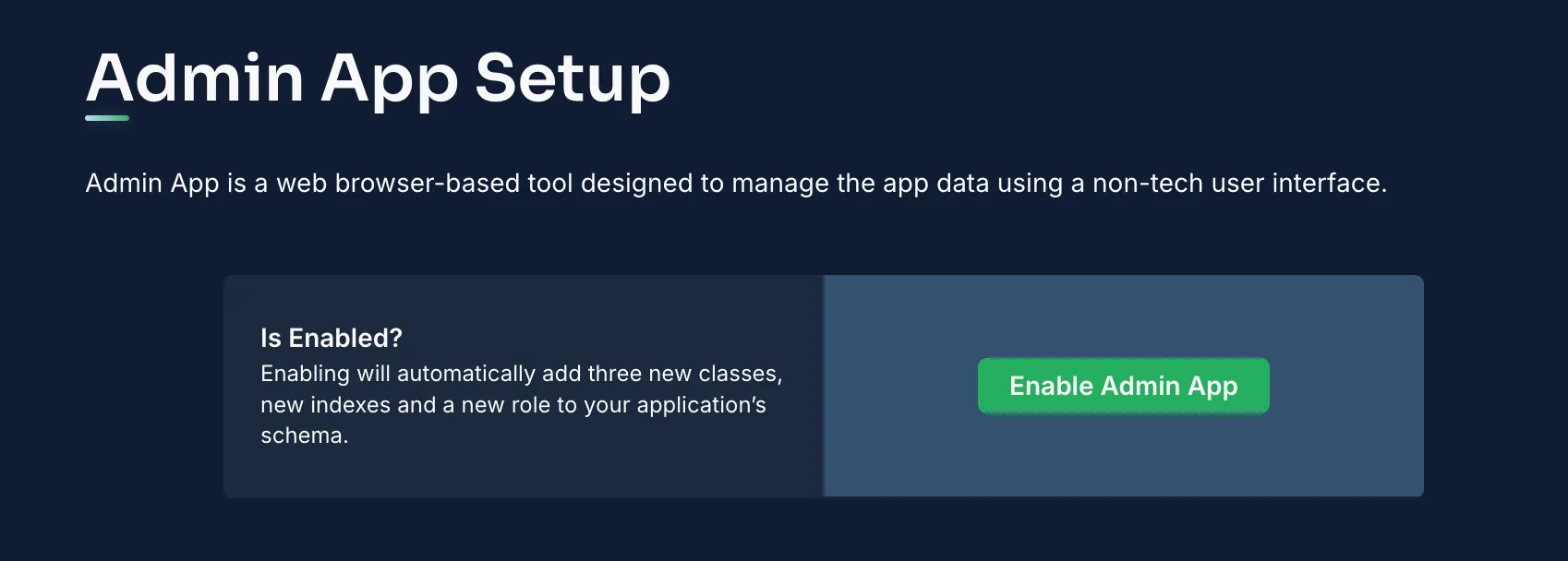
Once activated, log into the Admin App to manage your collections effortlessly.
In the Admin App, you can:
- Add Records: Click “Add Record” in any collection (e.g., Items) to create new entries.
- View/Edit Records: Select records to inspect or modify details.
- Remove Records: Delete entries that are no longer required.
This straightforward tool streamlines the process of performing basic data operations.
With your backend configured, it’s time to link your Deno frontend using REST or GraphQL APIs.
We will rely on API calls to interact with Back4app.
Create a module (e.g., fetchItems.ts) with the following code:
Integrate such API calls into your Deno application as needed.
Protect your data by assigning ACLs to each object. For instance, to ensure an item is private:
Within the Back4app dashboard, adjust CLPs for each collection to define default access policies, ensuring that only authenticated or authorized users can access or modify sensitive data.
Back4app uses the Parse User class for authentication. In your Deno application, manage user registration and login via REST API calls.
This approach can similarly be applied to login and session management.
Back4app’s Web Deployment feature allows you to host your Deno-based frontend by deploying code directly from a GitHub repository.
- Open your project directory in the terminal.
Run the build command: For example, if using a bundler like esbuild:
Bash1deno run --allow-read --allow-write build_script.ts- Confirm the Build Output: Ensure the output directory (e.g., dist) contains the necessary static files like index.html, bundled JavaScript, CSS, and images.
Your repository should include all source files for your Deno frontend. An example structure might be:
Initialize Git:
Bash1git initStage all files:
Bash1git add .Commit your changes:
Bash1git commit -m "Initial commit for Deno CRUD frontend"Push to GitHub: Create a repository (e.g., Basic-CRUD-App-Deno) and push:
Bash1git remote add origin https://github.com/your-username/Basic-CRUD-App-Deno.git 2git push -u origin main
- Log into Back4app and navigate to your project.
- Click on the Web Deployment feature.
- Connect your GitHub account following the prompts.
- Select your repository and branch (e.g., main) that holds your Deno code.
Specify:
- Build Command: If no pre-built dist folder exists, set the command (e.g., deno run --allow-read --allow-write build_script.ts).
- Output Directory: Define the output folder, such as dist.
- Environment Variables: Add any necessary environment variables (e.g., API keys).
To deploy with Docker, include a Dockerfile in your project:
Choose the Docker deployment option in Back4app if you prefer containerization.
- Initiate Deployment: Click the Deploy button in your Back4app dashboard.
- Monitor the Process: Back4app will fetch your code, execute build steps, and deploy your app.
- Access Your Site: After deployment, a URL will be provided where your Deno application is live.
- Visit the Provided URL: Open the URL in your browser.
- Test Your Application: Ensure that all routes, static assets, and API endpoints function correctly.
- Troubleshoot: If issues appear, consult the deployment logs and verify your configuration.
Congratulations! You have successfully built a basic CRUD application using Deno with Back4app as your backend.
You set up the project Basic-CRUD-App-Deno, structured your database, managed data through the Admin App, connected your Deno frontend via API calls, and secured your data with ACLs and CLPs.
Future Enhancements:
- Expand the Frontend: Add features like detailed views, search filters, or real-time updates.
- Advanced Backend Logic: Integrate Cloud Functions or additional API integrations.
- Deepen Security: Explore role-based access and further authentication measures.
For more details, check the Back4app documentation and explore additional resources.
Happy coding and enjoy building your scalable Deno CRUD application!
